Background
Cynefin Framework classifies Four Type of Problems
IdeaGens is focussed on Complex Problems
Simple problems can be easily defined, understood, and solved.
They typically have a clear cause and effect relationship and can be resolved with straightforward, well-established methods or techniques.
Problem: Car does not start
Analysis: Battery discharged, out of fuel, etc.
Complicated problems are technical. They have a straight-line, step-by-step solution and tend to be predictable.
Techniques like Six Sigma and process/product improvements are helpful.
Problem: Manufacturing of new car model
Analysis: Manufacturing methods, Quality Control, etc.
Complex problems are those that have multiple interconnected elements or factors, making them difficult to understand, analyze, or solve.
They often involve high levels of uncertainty, ambiguity, and unpredictability, and can have far-reaching consequences that affect multiple domains
IdeaGens.Com specializes in complex problems, requiring creativity and collaboration.
Problem: Introducing a new car brand/model
Analysis: PESTLE, Five Forces, SWOT, etc.
Chaotic problems are those that are characterized by a high degree of unpredictability and instability, making them difficult to understand and control.
Problem: Sudden multi-vehicle collision/pile-up
Analysis: Occurrences impossible to predict and prevent
Overview
High-Level
IdeaGens is a platform that includes multiple - applications, processes, and technologies.
Applications include assumption analysis, cause & effect analysis, idea generation, and others.
Processes include a 3-Phase/6-Step problem-solving process and others.
Technologies include AI input, manual input, instant visualization, and others.
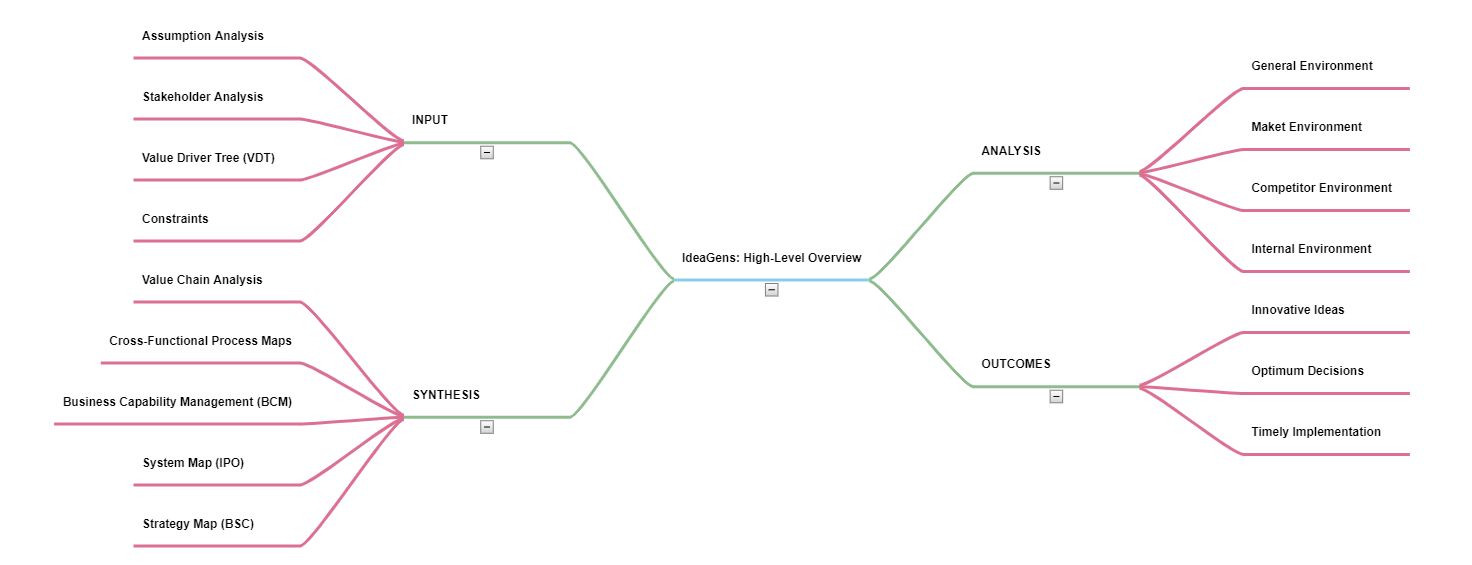
IdeaGen's problem-solving process can also be broken into four individual parts - INPUT, ANALYSIS, SYNTHESIS, and OUTCOMES, as visualized below:
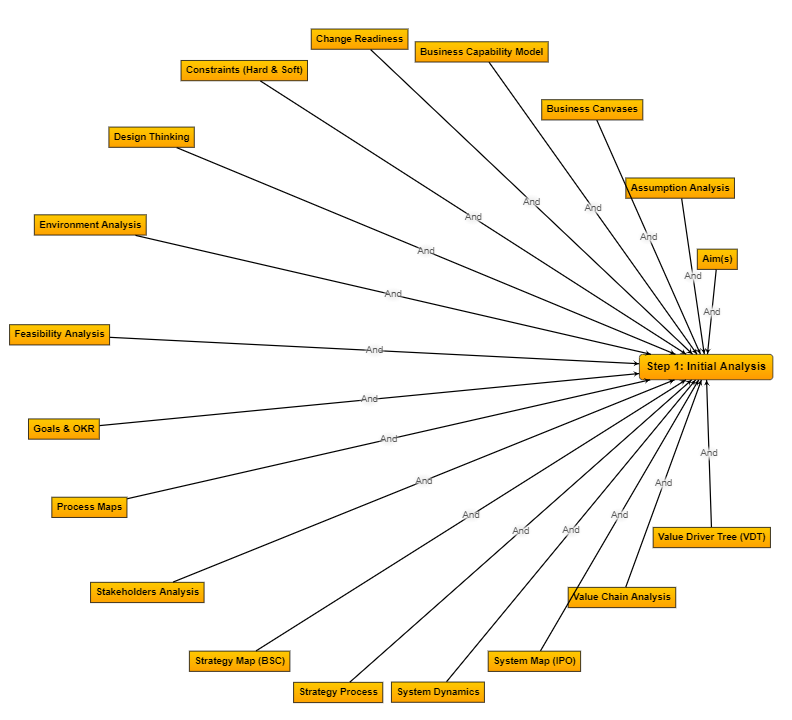
Step 1:
Initial Analyses
It starts with understanding the "true or real" problem.
"If I had one hour to solve a problem, I would spend 55 minutes thinking about the problem and 5 minutes thinking about solutions," - attributed to Einstein.

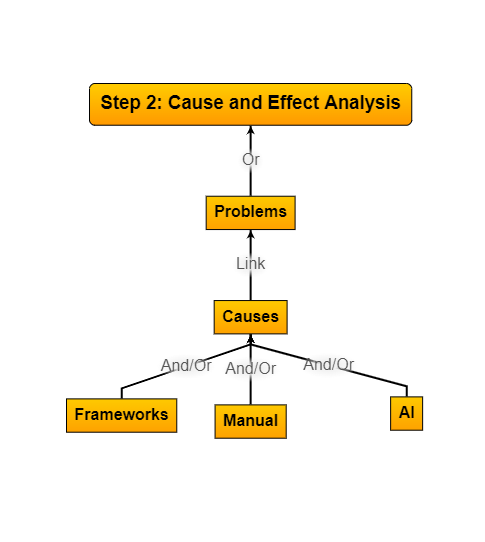
Step 2:
Cause & Effect Analysis
Critical Reasons for Separating Causation from Correlation:
Avoiding False Conclusions, Understanding True Relationships, Effective Problem-Solving, Avoiding Spurious Relationships, Informed Decision-Making, and Accurate Predictions and Interventions.

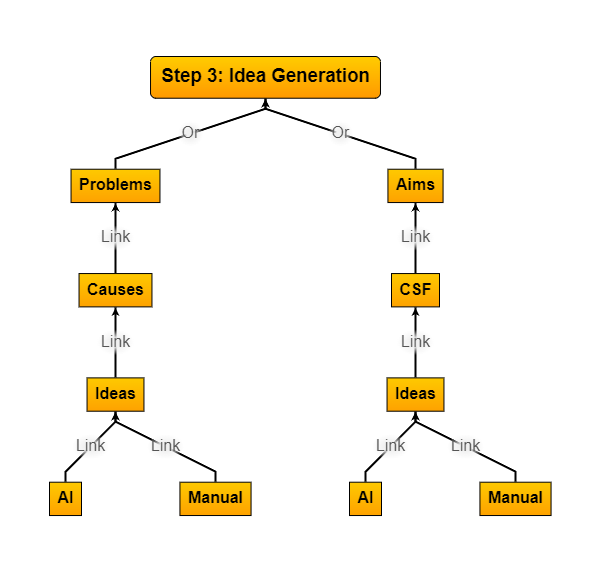
Step 3:
Idea Generation or Ideation
Ideation, the process of generating and developing new ideas, is critical to solving complex problems for several key reasons:
Encourages Creativity and Innovation, Explores Multiple Solutions, Breaks Down Complexity, Fosters Collaboration, Enhances Adaptability and Flexibility, Promotes Risk Mitigation, Increases Engagement and Motivation, and Builds a Culture of Continuous Improvement.

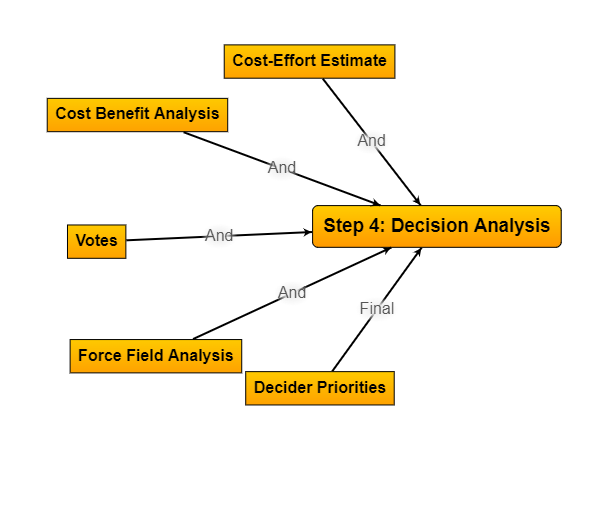
Step 4:
Decision Analysis
Here are several vital reasons why Decision Analysis is essential:
Structured Decision-Making Process, Managing Uncertainty, Balancing Multiple Objectives, Facilitating Communication and Collaboration, Improving Decision Quality, Optimizing Resources, Scenario Planning and Flexibility, and Accountability and Documentation.

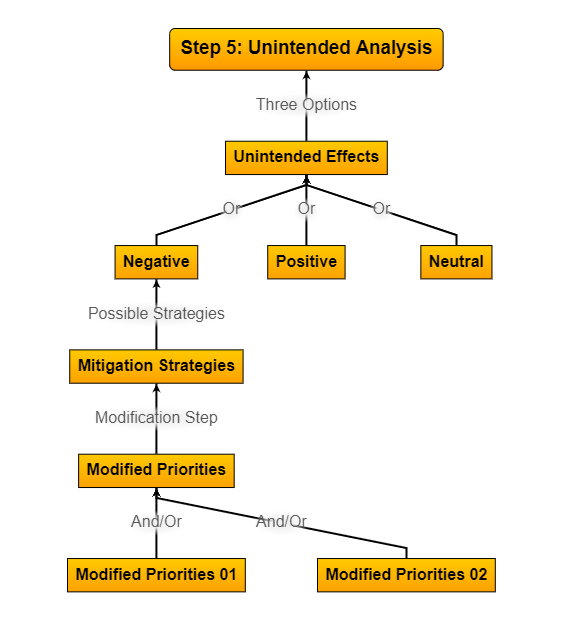
Step 5:
Unintended Analysis
Anticipating The Law of Unintended Consequences is critical in solving complex problems for several key reasons:
Revealing Hidden Factors, Preventing Oversights, Encouraging Creative Thinking, Mitigating Unintended Consequences, Enhancing Problem Understanding, Adapting to Dynamic Environments, Fostering Interdisciplinary Insights, Supporting Risk Management and Improving Decision-Making.

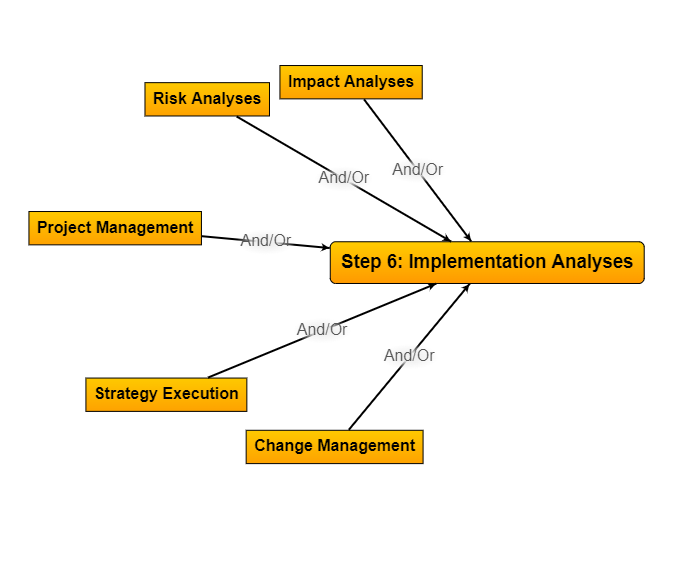
Step 6:
Implementation Analysis
Application of multiple techniques, to greatly increase implementation success.